Understanding Singapore-US Stock Capital Gain Tax Implications
Investing in international stocks can be a lucrative venture, but it's crucial to understand the tax implications, particularly when dealing with cross-border investments. This article delves into the Singapore-US stock capital gain tax, offering insights into how these transactions are taxed and the potential impact on your investment returns.
What is Singapore-US Stock Capital Gain Tax?
The Singapore-US stock capital gain tax refers to the tax imposed on the profit realized from the sale of stocks held in a Singaporean company that is listed on a U.S. stock exchange. This tax is applicable to both individuals and corporations and is governed by the tax treaties between Singapore and the United States.
Tax Rates and Treaties
The tax rate for Singapore-US stock capital gain varies depending on the nature of the investor and the specific provisions outlined in the tax treaties. Generally, the tax rate is 15% for individuals and 30% for corporations. However, certain conditions and exceptions may apply.
Tax Calculation
To calculate the capital gain tax, you need to determine the cost basis of the stock. This is the original purchase price plus any additional costs, such as brokerage fees. The selling price of the stock is then subtracted from the cost basis to determine the capital gain.
Example:
Suppose you purchased 100 shares of a Singaporean company listed on the U.S. stock exchange for
Reporting and Compliance
Investors must report their capital gains from Singapore-US stock transactions on their U.S. tax returns. Failure to comply with these requirements can result in penalties and interest.
Tax Planning Strategies
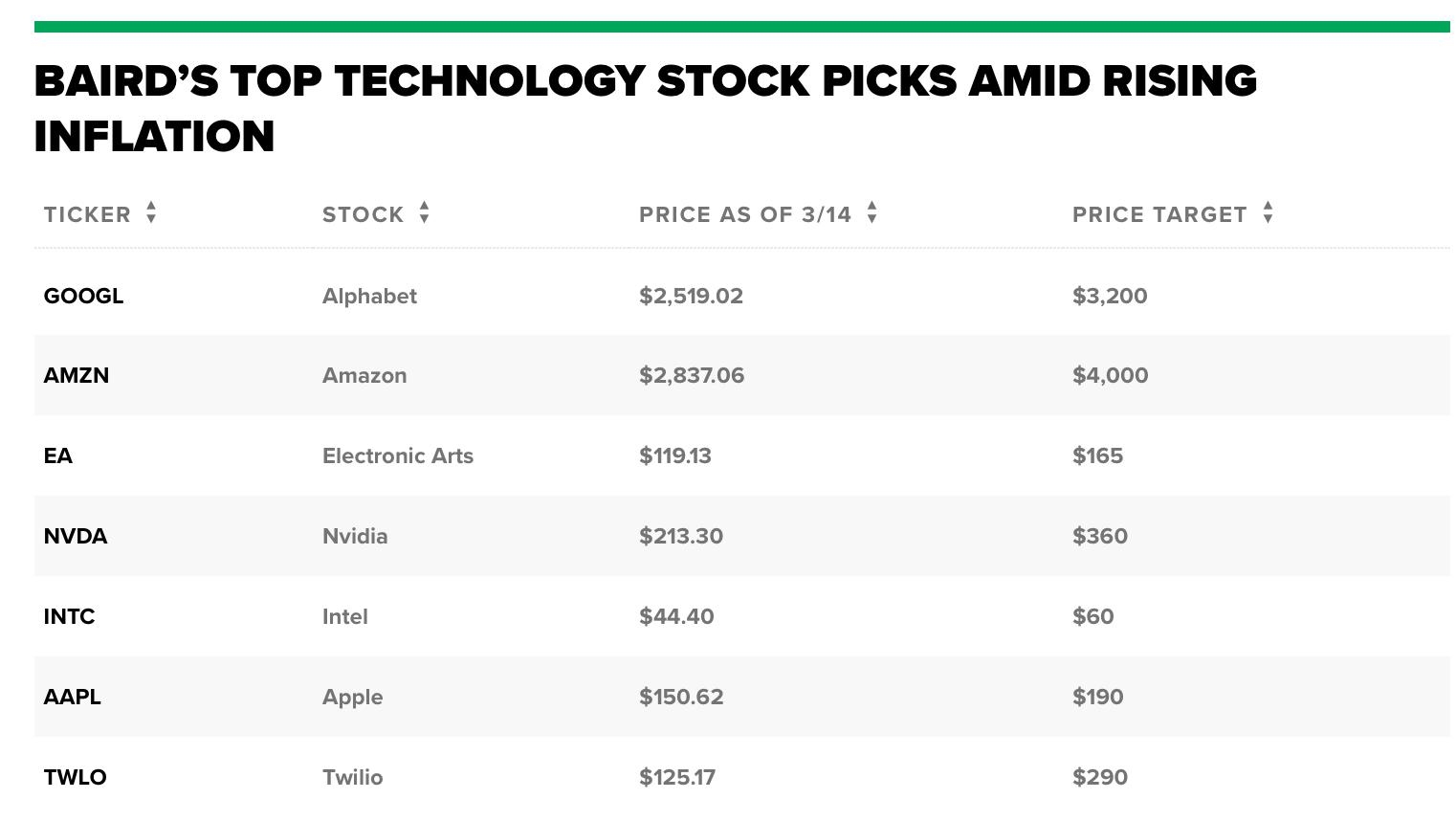
Understanding the Singapore-US stock capital gain tax can help investors implement effective tax planning strategies. Here are a few tips:
- Diversify your portfolio: By diversifying your investments, you can potentially reduce your overall tax liability.
- Consider tax-efficient structures: Utilize tax-efficient structures, such as retirement accounts or tax-deferred accounts, to minimize your tax burden.
- Stay informed: Keep up-to-date with the latest tax laws and regulations to ensure compliance.
Case Study:
Let's consider a hypothetical scenario involving an American investor named John. John purchased 500 shares of a Singaporean company listed on the NASDAQ for
John's capital gain tax would be
Conclusion
Understanding the Singapore-US stock capital gain tax is essential for investors looking to invest in international stocks. By familiarizing yourself with the tax laws and implementing effective tax planning strategies, you can maximize your investment returns while minimizing your tax liability.
us stock market today live cha
like
- 2026-01-18US Momentum Stocks: Top Performers Over the Past 5 Days in August 2025
- 2026-01-20How Major US Stock Indexes Fared on April 8, 2025"
- 2026-01-15Title: US Election Results and Their Impact on the Stock Market
- 2026-01-16Title: US Blue Chip Stocks 2016: A Comprehensive Overview
- 2026-01-15Understanding the US Dollar Stock Symbol: A Comprehensive Guide
- 2026-01-18Top Momentum US Stocks Today: A Deep Dive into the Market's Hot Picks
- 2026-01-20JPMorgan's Dimon Warns of Inflated US Stock Market
- 2026-01-17Hot US Stocks to Watch in July 2025
- 2026-01-18QCOM US Stock Price: What You Need to Know
- 2026-01-15How to Buy US OTC Stocks in the UK
