Understanding PE Ratio: A Comprehensive Guide to US Stock Valuation
In the world of investing, the PE ratio (Price-to-Earnings ratio) is a crucial metric for analyzing the valuation of stocks. For investors in the United States, understanding how to interpret and utilize the PE ratio can significantly enhance their decision-making process. This article aims to provide a comprehensive guide to the PE ratio, its importance in the US stock market, and how to effectively use it for investment purposes.
What is the PE Ratio?
The PE ratio is a financial ratio that compares the price of a stock to its per-share earnings. It is calculated by dividing the current stock price by the company's earnings per share (EPS). The formula is as follows:
[ \text{PE Ratio} = \frac{\text{Stock Price}}{\text{EPS}} ]
For example, if a stock is trading at
Interpreting the PE Ratio
The PE ratio can provide valuable insights into a company's valuation. Here's how to interpret it:
- Low PE Ratio: A low PE ratio may indicate that a stock is undervalued. This could be due to a variety of factors, such as market sentiment, industry trends, or company-specific issues.
- High PE Ratio: Conversely, a high PE ratio may suggest that a stock is overvalued. This could be due to strong earnings growth prospects, high demand for the stock, or a positive outlook for the industry.
- Average PE Ratio: The average PE ratio for the overall market can serve as a benchmark for comparison. If a stock's PE ratio is significantly lower or higher than the market average, it may indicate undervaluation or overvaluation.
Using the PE Ratio for Investment Decisions
The PE ratio can be a valuable tool for investors, but it should be used in conjunction with other metrics and fundamental analysis. Here are some ways to use the PE ratio for investment decisions:
- Comparative Analysis: Compare the PE ratio of a company to its peers in the same industry. This can help identify undervalued or overvalued stocks within the industry.
- Historical Analysis: Analyze the historical PE ratio of a company to understand its valuation trends over time.
- Market Analysis: Compare the PE ratio of a company to the overall market to determine if it is undervalued or overvalued relative to the market.
Case Studies
To illustrate the use of the PE ratio, let's consider two hypothetical companies:
- Company A has a PE ratio of 15, while the industry average is 20. This suggests that Company A may be undervalued.
- Company B has a PE ratio of 25, significantly higher than the industry average of 20. This indicates that Company B may be overvalued.
By analyzing the PE ratios of these companies, investors can make more informed decisions about their investments.
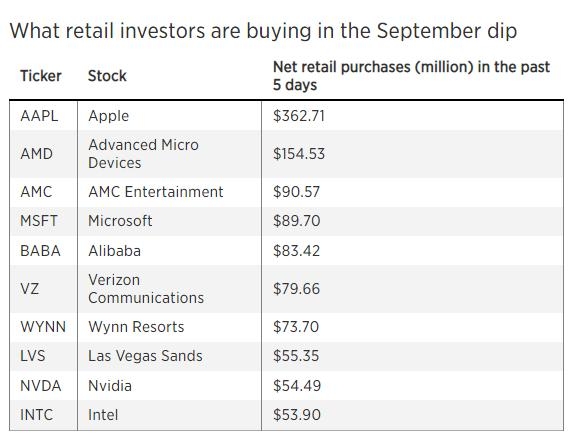
Conclusion
The PE ratio is a powerful tool for analyzing the valuation of stocks in the US stock market. By understanding how to interpret and use the PE ratio, investors can make more informed decisions and potentially enhance their investment returns. Remember to use the PE ratio in conjunction with other metrics and fundamental analysis for a comprehensive investment strategy.
api us stock
like
- 2026-01-21How Foreigners Can Invest in the US Stock Market: A Comprehensive Guide"
- 2026-01-18Best Platform to Buy US Stocks in Canada: Your Ultimate Guide
- 2026-01-21Unlock the Power of CFD Trading in US Stocks
- 2026-01-15Best US Stocks in 2015: A Look Back at the Market's Top Performers
- 2026-01-16Lly Us Stock: Your Ultimate Guide to Understanding and Investing in Stock Market
- 2026-01-22Roomba Front Wheel Caster US Stock: Top Options for Robotic Vacuum Cleaners
- 2026-01-20Islamic US Stock Online Broker: Your Ultimate Guide to Halal Investing
- 2026-01-18Broadcom US Stocks: A Comprehensive Guide to Investing in This Tech Giant
- 2026-01-16Buy Us Stocks with USDT: A Guide to Cryptocurrency Investing
- 2026-01-21http stocks.us.reuters.com stocks fulldescription.asp rpc 66&symbol bdx: Unveiling the Power of BDX Stocks
