Average Stock Wealth in the US: A Comprehensive Analysis
In the ever-evolving landscape of the American financial market, understanding the average stock wealth is crucial for investors and policymakers alike. This article delves into the average stock wealth in the US, examining its trends, factors influencing it, and its implications for the economy.
Trends in Average Stock Wealth
The average stock wealth in the US has seen significant fluctuations over the years. According to the Federal Reserve's Survey of Consumer Finances, the median net worth of a household increased from
Factors Influencing Average Stock Wealth
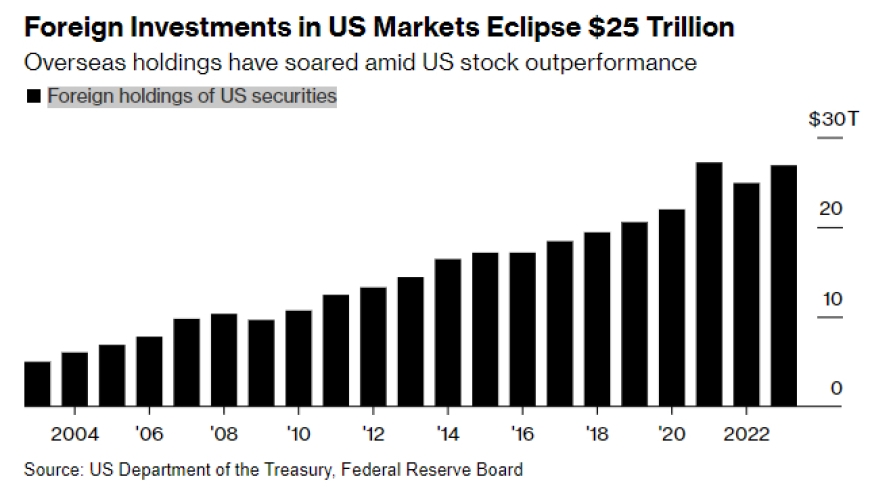
Several factors contribute to the average stock wealth in the US. One of the primary factors is the stock market's performance. Over the past few decades, the US stock market has experienced significant growth, leading to increased wealth for investors. Additionally, factors such as demographic shifts, tax policies, and economic conditions play a crucial role in shaping the average stock wealth.
Demographic Shifts
Demographic shifts, particularly the aging population, have had a significant impact on the average stock wealth. As baby boomers approach retirement, they are more likely to hold stocks, which contributes to the overall stock wealth. However, the younger generation, particularly millennials, has a lower propensity to invest in stocks, which could impact future stock wealth trends.
Tax Policies
Tax policies also play a crucial role in shaping the average stock wealth. For instance, the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act of 2017 reduced corporate tax rates, leading to increased corporate profits and stock prices. This, in turn, has contributed to the overall stock wealth in the US.
Economic Conditions
Economic conditions, such as interest rates and inflation, also influence the average stock wealth. For instance, low-interest rates can lead to increased borrowing and investment, which can drive up stock prices. Conversely, high inflation can erode purchasing power and negatively impact stock wealth.
Case Studies
To illustrate the impact of these factors, let's consider a few case studies. During the dot-com bubble of the late 1990s, the average stock wealth in the US surged as investors chased high-flying tech stocks. However, when the bubble burst, the average stock wealth took a significant hit. Another example is the financial crisis of 2008, which led to a sharp decline in the stock market and, consequently, a decrease in average stock wealth.
Conclusion
Understanding the average stock wealth in the US is essential for investors and policymakers. By examining the trends, factors influencing it, and its implications for the economy, we can gain valuable insights into the American financial market. As the landscape continues to evolve, staying informed about these factors will be crucial for making informed decisions.
us stock market today
like
- 2026-01-18Stock Options: IFRS vs. US GAAP
- 2026-01-16Buy Us Stocks Malaysia: A Strategic Guide to Investing in Malaysian Equity Markets
- 2026-01-22August 11, 2025: US Stock Market Performance Analysis
- 2026-01-22US Stock M7: A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding and Investing in This Unique Market
- 2026-01-16Does Japan Nintendo Stock Affect US Nintendo Stock?
- 2026-01-20US Airline Stocks: A Comprehensive Guide to Investment Opportunities"
- 2026-01-17Title: US Stock Market All-Time Graph: A Comprehensive Overview
- 2026-01-23Dow to Crash: What You Need to Know About the Potential Market Downturn
- 2026-01-20US Stock Market Bailout: The Essential Guide to Understanding Its Impact
- 2026-01-15Best US Penny Stocks to Buy in 2017: A Guide to High-Potential Investments
